Given the tremendous growth of cyber threats today has not only caused an impact on personal data but also boosted the rise of the cost of a single breach. A recent report by IBM revealed that the average cost of a data breach had risen 12 percent over the past five years to $3.92 million per incident on average. The report does not only put it that cyber incidents are just increasing and their cost increasing, but also can last for longer periods unnoticed.
Why do Data breaches continue Rising?
As of this digital era, cyber-incidents represent a huge opportunity for big money to Cybercriminals, but as this is a great opportunity for cybercriminals, on the other side it equates to significant losses for enterprises, unfortunately. According to some of the cybersecurity reports from our Summit Frontliners and already known stats, below is a graphical representation of some of the reasons why cyber-incidents keep rising.
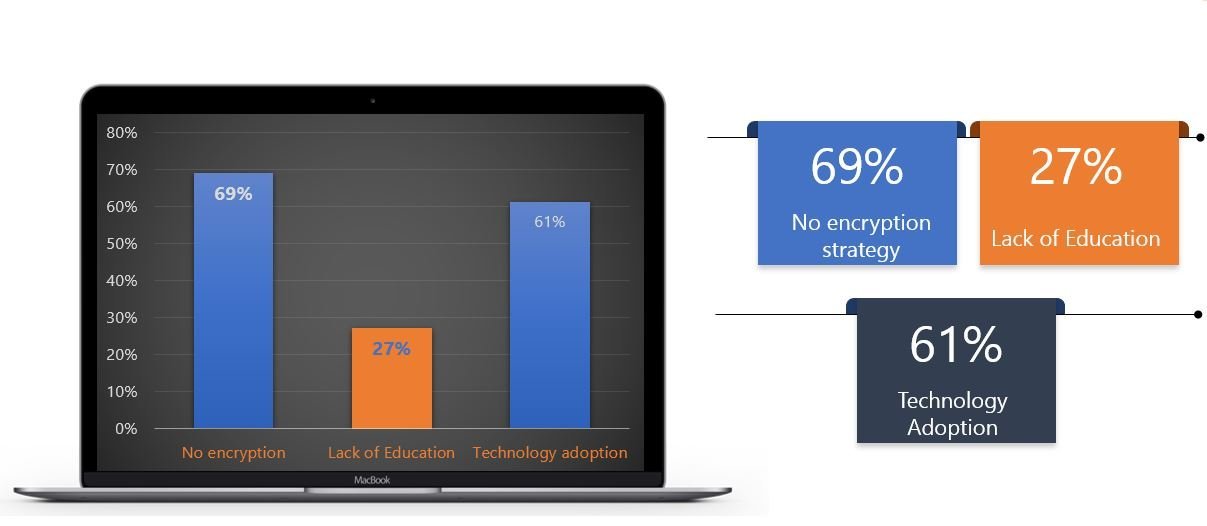
According to the statistics by our security experts show that most enterprises do not take appropriate steps to protect their critical information. For instance, in cyberspace data is said to be secure if it is made unreadable (encrypted) to others and this can prevent discovered data from being stolen. But to our surprise, most of these organizations do not have encryption strategies in place.
Additionally, Human error arising from lack of awareness on basic cyber-hygiene continues to be a factor, as does the lack of understanding of risks by leaders and executives. Enterprises need to understand that in this new normal, they cannot remain stagnant but adopt the cyber-resilience campaigns, particularly as hackers continue to evolve.
We also noted that the rise of cyber-crime is largely attributed to increased reliance and technology adoption, this has in a way increased the company’s vulnerability, but also to note, hackers are rapidly adapting to new trends such as data mining and AI for which they target a range of victims from the cloud to access data.
The Cost of cybercrime also Rises

As the world adapts to the new normal in 2020, cybercrime statistics are set to increase significantly. Economies are dependent on computer networks and information technology matrices. Cyberattacks have become more attractive and costly. For organizations and individuals alike, protecting data is business-critical – especially in light of the shift towards remote working in 2020.
Many institutions report cybercrime losses under operating expenses thereby increasing the costs of operations and giving a bad jaws-ratio. According to ACFE.com, an average company loses about 5% of its annual revenue to fraud. Based on our summitFRONTLINE experience, we estimate about 3% of the total fraud loss is cyber breach-related. Applied to the Uganda National Budget 2020, of Ugx 40.487 trillion, that translates into Ugx. 1.215 trillion annual loss nationally due to cybercrime.
So to this end, there is no such thing as 100% cybersecurity! Cyberthreats are always evolving as technology evolves. But what distinguishes cyber-resilient entities from the cyber-prone ones is the right knowledge, total ownership for the cybersecurity strategy from the topmost leadership, the embrace of good cyber hygiene through budget allocation to develop capabilities for defensive and offensive cyber capabilities, and agile threat management best practices.
In this presentation, we will break-down a network intrusion step-by-step strategy for cybercriminals into six phases. This is purposed to bring an awareness of how an intrusion is conducted and prior detection measures that can prevent an attacker from moving between phases. Those stages are as follows:
1. Reconnaissance;
 Before any cybercriminal gets to you or your critical data, they work out all means to understand their target and this marks the first stage of any intrusion. In the effort to understand their targets, they perform a series of activities which include; scanning for important people and their email addresses, looking up open-source information regarding targeted organizations, and documenting all their milestones on the targeted network.
Before any cybercriminal gets to you or your critical data, they work out all means to understand their target and this marks the first stage of any intrusion. In the effort to understand their targets, they perform a series of activities which include; scanning for important people and their email addresses, looking up open-source information regarding targeted organizations, and documenting all their milestones on the targeted network.
The worst scenario so happens when network defenders do not know what technologies malicious people intend to use on a network and yet attackers know what’s actually in use on the targeted network. The severity of the matter is criminals spend time learning the security functionalities of the devices on the network and get to know the vulnerabilities on them and how to exploit them.
Caution: Now, at this intrusion phase, defenders can stop the intrusion if they invest the time and energy necessary to understand their own devices on the network and to familiarize themselves with those products’ security functionalities.
2. Exploitation;
 In the instance, that network defenders fail to detect and stop cybercriminals during or after reconnaissance, then it allows hackers to look for an initial exploitation vector by which they can gain access to their target’s network. It is from attack-vectors like spear-phishing, watering-hole attacks, exploiting a known CVE vulnerability, or conducting SQL injection that criminals succeed in exploiting the target network.
In the instance, that network defenders fail to detect and stop cybercriminals during or after reconnaissance, then it allows hackers to look for an initial exploitation vector by which they can gain access to their target’s network. It is from attack-vectors like spear-phishing, watering-hole attacks, exploiting a known CVE vulnerability, or conducting SQL injection that criminals succeed in exploiting the target network.
Caution: Cybercriminals can never go beyond this phase if the IT security team continually updates their network inventory (software and hardware) using common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) information and make sure their networks aren’t relying on users to always make the right decisions.
3. Establish Persistence;
 Attackers who successfully go past achieve initial exploitation phase ultimately seek to establish persistence in the network. This is accomplished when they escalate privileges, finding the Run Keys, or getting into scripts.
Attackers who successfully go past achieve initial exploitation phase ultimately seek to establish persistence in the network. This is accomplished when they escalate privileges, finding the Run Keys, or getting into scripts.
Caution: with the mind that you got an intruder on the network is like a feeling when you have a burglar inside the house and the only way to prevent them from doing anything harmful, if at all they have not done that already, is by practicing application whitelisting. Most organizations have assets that should be protected and segmented off from the rest of the network. When you utilize this methodology, you restrain the attackers from running malware or something unusual on those business-critical assets.
4. Install Programs and or Tools
As long as attackers get access to organizational networks and remain persistent or have an assurance that they can hang around in a network and not get caught, then with these privileges, they can initiate their malicious activity by installing malicious programs that perform malicious activities like Ransomware, Rootkits, spyware, keyloggers, all kinds of trojans among others.
Caution: Now to the IT security team, if a program has been run for the first time or second time public web, then it would be a good idea to prevent that item from running. Additionally, reputation services can also help block attackers from communicating not only with known malicious domains but also suspect domains that don’t have a good reputation.
5. Locate and navigate the network
 Once attackers successfully install their tools that perform in the interest of their aims, then cyber criminals will begin moving around the entire network to locate their interests (sensitive information) With the help of their installed tools.
Once attackers successfully install their tools that perform in the interest of their aims, then cyber criminals will begin moving around the entire network to locate their interests (sensitive information) With the help of their installed tools.
Caution: When you segment and monitor your network, together with restricting privileges, enabling two-factor authentication on all accounts, and creating processes that can help ensure the security of a remote connection, then you will have at least an information security assurance
6. Exfiltrate Sensitive data
 When cybercriminals have the freedom of navigating the network and locate what they need, then they completely have their target at hand and all they need to do is get what they need and leave undetected.
When cybercriminals have the freedom of navigating the network and locate what they need, then they completely have their target at hand and all they need to do is get what they need and leave undetected.
Caution: No enterprise would wish to make the news headlines the next day for a data breach after attackers uploading their sensitive information to the public. It is for this reason that enterprises empower their IT security teams to make sure that they have processes in place that monitor for unusual data transfers or malicious traffic. Also to avoid being held ransom and asked for huge sums of money from cybercriminals, Enterprises should invest in backup plan strategies to enable the company to operate during the time of cyber-incidents where hackers steal or erase a target’s data.
Conclusion
As of today, It has been proved beyond all security potential that enterprises can’t protect themselves from every form of intrusion. But if in their capacity can know well the devices they use, and how to deploy all the security measure available to them with a mind that an intrusion could happen at any point in time on their network, they will be better equipped to detect an intrusion and prevent attackers from stealing valuable information.

